|
|
Why do cars use both ceramic and metal catalysts?(source: www.gaslyst.com)
Automotive exhaust emissions are a key issue in global environmental protection. To reduce the emission of harmful gases, catalysts are widely used in automotive exhaust purification systems. The carrier materials for these catalysts are mainly divided into two categories: ceramic and metal. Why do cars use both of these materials? This article will analyze this from the perspective of principles, material characteristics, advantages and disadvantages, and application scenarios.
I. Basic Principles of Catalysts
The main function of automotive catalysts is to convert harmful gases in exhaust (CO, carbon monoxide; HC, hydrocarbons; NOx, nitrogen oxides) into harmless gases (CO₂, water, N₂).
A catalyst usually consists of two parts:
1. Support: Provides a high specific surface area, allowing the precious metals to be evenly dispersed.
2. Active Component: Generally precious metals, such as platinum (Pt), palladium (Pd), and rhodium (Rh), responsible for catalyzing chemical reactions.
The catalyst accelerates the conversion of harmful gases in the exhaust through surface reactions without being consumed itself.
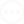
II. Ceramic Catalysts
1. Materials and Structure
Ceramic catalysts generally use aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) or aluminum oxide-titanium mixed materials as carriers, adopting a honeycomb or plate structure with uniform pores and a large surface area, which is conducive to the dispersion of precious metals.
2. Advantages
• High temperature resistance: Can withstand high temperatures above 800°C, and is not easy to melt or deform.
• Good chemical stability: Corrosion resistance, aging resistance, and long service life.
• Relatively low cost: Ceramic materials are inexpensive and easy to mass-produce.
3. Disadvantages
• High brittleness: Poor shock resistance, easily broken under strong bumps or impacts.
• Poor thermal conductivity: Heats up to working temperature slowly, and is not as effective as metal carriers for low-temperature start-up emission control.
4. Application Scenarios
• Heavy-duty vehicles, high-speed vehicles.
• High-temperature exhaust environments, such as catalysts for diesel vehicle DPF (diesel particulate filter). III. Metal Catalysts
1. Materials and Structure
Metal catalyst carriers are generally made of stainless steel or nickel-based alloys in a metal honeycomb structure, coated with an alumina layer, and then loaded with precious metals. 2. Advantages
• Good vibration resistance: Metal materials have high toughness and are not easily broken, making them suitable for engines with significant vibration.
• Good thermal conductivity: They can quickly heat up to the catalytic reaction temperature, especially providing excellent emission control during the cold start phase.
• Flexible structure: They can be manufactured into complex shapes, suitable for engine compartment designs with limited space.
3. Disadvantages
• Slightly poorer high-temperature resistance: Oxidation or deformation may occur in extremely high-temperature environments.
• Higher cost: The cost of metal materials and processing is higher than that of ceramics.
4. Application Scenarios
• Passenger cars, especially small cars or hybrid vehicles.
• Cold start emission control in low-temperature exhaust environments.
IV. Comparison Summary of Ceramic and Metal Catalysts
Characteristics Ceramic Catalyst Metal Catalyst
High-temperature resistance High Medium
Vibration resistance Poor High
Thermal conductivity Poor High
Production cost Low High
Applicable environment High temperature, long-term operation Cold start, high vibration
V. Why Do Cars Use Both Types of Catalysts Simultaneously?
1. Balancing high-temperature resistance and rapid start-up: Ceramic catalysts are suitable for high-speed and long-term high-temperature operation, while metal catalysts are suitable for cold start and low-temperature operation.
2. Optimizing exhaust purification efficiency: The combination of the two materials can achieve optimal exhaust purification effects under different temperatures and driving conditions.
3. Extending lifespan and reliability: The toughness of the metal catalyst can protect the brittle ceramic catalyst, reducing the risk of breakage.
VI. Conclusion
The use of both ceramic and metal catalysts in automobiles is to achieve the best exhaust purification effect under different operating conditions. Ceramic catalysts are high-temperature resistant and low-cost, but brittle; metal catalysts have strong vibration resistance and fast heat conduction, but are more expensive. Combining the two ensures both emission control and extended catalyst lifespan, making it an important choice in modern automotive exhaust treatment technology.
|
|
![]() ASK & HELP
38 Read
|
0 Reply
|
2026-01-07
ASK & HELP
38 Read
|
0 Reply
|
2026-01-07